Technical Vs. Fundamental Analysis in Stock Trading
So you’ve decided to enter the exciting and often nerve-racking world of stock trading. Awesome! But, before you get into buying and selling stocks, you must first learn the tools of the trade: technical analysis and fundamental analysis. These two approaches, which are separate but mutually beneficial, are the keys to revealing profitable possibilities in the stock market’s ever-changing landscape.
Beginning a stock trading adventure entails navigating through several strategies, with technical and fundamental analysis serving as pillars in the area of market analysis. This blog addresses the details of these two approaches and their importance in the fast-paced world of stock trading.
Decoding Technical Analysis In Stock Trading
Imagine being able to foresee the future simply by looking at curving lines on a graph. That is the core concept of technical analysis. Technical analysts examine historical market data and chart patterns to estimate future price changes. This method looks at past price movements and volume data to uncover patterns and trends that can be used to estimate future stock values.
Key Tools Of Technical Analysis In Stock Trading
In technical analysis, some key tools are used, which are mentioned below:
- Charting: Technical analysts study charts attentively, reviewing trends, support and resistance levels, and numerous chart patterns such as head and shoulders or double bottoms. These patterns, generated by prior price movements, are thought to provide insight into future price direction.
- Technical Indicators: Moving averages, the Relative Strength Index (RSI), Bollinger Bands, and various other indicators are used to assess momentum, volatility, and probable overbought or oversold levels in a stock. Traders hope to make informed purchasing and selling decisions by analyzing these indications alongside price charts.
- Market sentiment: To comprehend the overall mood of the market and its potential impact on individual stocks, technical analysts also evaluate broader market sentiment, which is commonly gauged by indexes or investor surveys.

Strengths Of Technical Analysis
The benefits of technical analysis are:
- Visual Representation: Technical analysis employs charts and patterns to provide a visual depiction of price changes. This helps traders discover trends, patterns, and potential entry/exit positions.
- Short-Term Forecasting: It is especially useful for short-term trading. Using technical indicators and charts, traders can profit from short-term price changes.
- Focus On Price Fluctuations: Technical analysis focuses entirely on price fluctuations, ignoring all other aspects. For traders who prefer a more direct approach, this simplicity can be advantageous.
- Market Psychology: Market psychology and sentiment are taken into account in technical analysis, representing the collective behavior of market players. This can provide useful information about probable future movements.
- Adaptability: Technical analysis is adaptable to a variety of trading strategies, including day trading, swing trading, and long-term investing. It provides a versatile foundation for traders with varying tastes.
Weaknesses Of Technical Analysis
Limitations of technical analysis are:
- Limited Information: Technical analysis does not take into account an asset’s fundamental value. It is based on previous price and volume statistics, ignoring important features of a firm or asset.
- Subjective Perception: Chart and pattern interpretation can be subjective, resulting in varied conclusions among traders. This subjectivity might lead to contradictory methods and judgments.
- Concentrating On Short-Term Movements: While technical analysis is valuable for short-term trading, it may overlook bigger economic patterns and long-term market swings, limiting its utility for long-term investors.
- Ignores Fundamental Factors: Technical analysis does not take into consideration fundamental aspects such as earnings, dividends, or market circumstances. Relevant news or events can have a significant impact on prices but are not taken into account in technical analysis.
- Inability In Unpredictable Markets: Technical analysis alone may not deliver reliable predictions in extremely unpredictable or news-driven markets. Technical signals can be overridden by unexpected events.
Decoding Fundamental Analysis In Stock Trading
While technical analysis is concerned with the surface of an organization, fundamental analysis goes deep into the core of an organization. This method attempts to determine a stock’s intrinsic value by examining the company’s financial health, business structure, marketplace competition, and future growth possibilities. It’s a longer-term strategy based on a stock’s intrinsic worth.
Key Tools Of Fundamental Analysis In Stock Trading
In fundamental analysis, some key tools are used, which are mentioned below:
- Financial Statements: Investors examine a company’s income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to determine its profitability, solvency, and liquidity. Earnings per share (EPS), price-to-earnings ratio (P/E), and debt-to-equity ratio are all useful indicators of a company’s financial health.
- Management Quality: A company’s management team’s qualifications, expertise, and track record are critical variables in determining its prospects. Investors seek strong leadership with a clear vision for the company’s future growth.
- Industry And Competitive Analysis: It is critical to understand the competitive environment of the industry in which a company works. Market share, competitive advantages, and possible disruptions can all have a substantial impact on a company’s future performance.
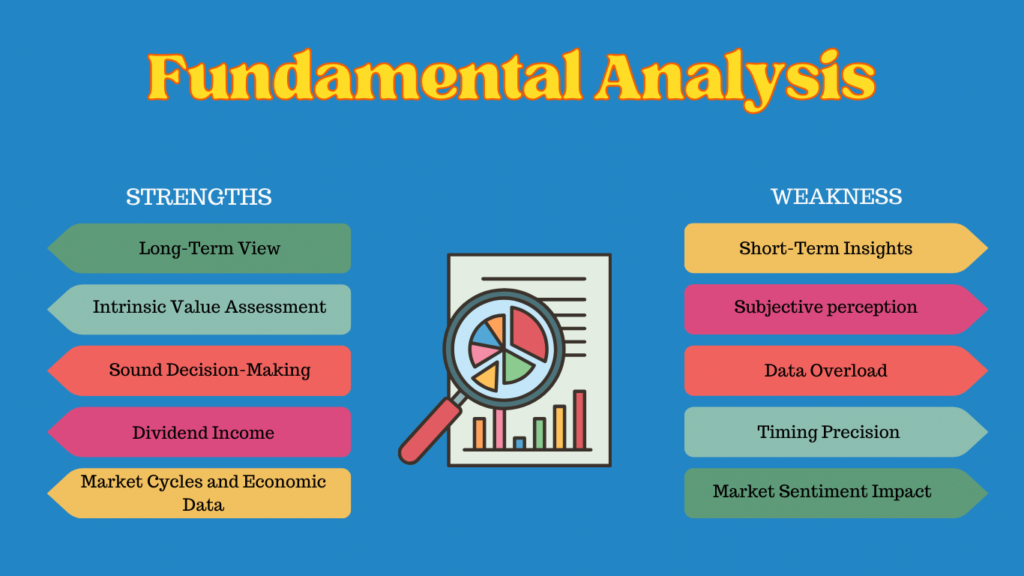
Strengths Of Fundamental Analysis
The benefits of fundamental analysis are:
- Long-Term View: Fundamental analysis is ideal for long-term investors since it focuses on a company’s fundamental value and its potential for long-term growth.
- Intrinsic Value Assessment: It assists in identifying a stock’s intrinsic value by assessing numerous basic criteria such as earnings, dividends, and financial health.
- Sound Decision-Making: Investors who use fundamental analysis base their conclusions on a company’s financial soundness, management competence, and development possibilities, allowing them to make more informed decisions.
- Market Cycles And Economic Data: Fundamental analysis considers economic data, industry trends, and market cycles to provide a comprehensive picture of overall market conditions.
- Dividend Income: For investors looking for a constant income stream from dividends, fundamental analysis can help them pick companies with a history of consistent dividend payouts.
Weaknesses Of Fundamental Analysis
Limitations of fundamental analysis are:
- Short-Term Insights: Because fundamental research focuses on a company’s long-term potential rather than short-term market swings, it may not provide reliable insights for short-term traders.
- Subjective Perception: Certain fundamental indicators might be subjective, and interpretations can differ amongst analysts, thereby leading to inconsistencies in the study.
- Data Overload: For newcomers to basic research, the sheer volume of financial data and ratios involved can be daunting, making it difficult to prioritize and comprehend information properly.
- Market Sentiment Impact: External influences, such as market mood, can often eclipse fundamental signs, resulting in differences between a stock’s intrinsic value and its market price.
- Timing Precision: Fundamental research may not provide accurate timing for market entry or exit, which is critical for traders using short-term or momentum-driven strategies.
The Winning Strategy: Combining Technical and Fundamental Analysis
In the complex world of stock trading, the combination of technical and fundamental analysis creates a powerful technique. Technical analysis excels at identifying good entry and exit positions, and assisting traders with trade timing. Fundamental analysis, on the other hand, provides a broader perspective, providing investors with a thorough grasp of a company’s financial health and growth possibilities.
Investors receive a comprehensive perspective by smoothly integrating these methodologies, which combine the art of timing with the science of intrinsic value assessment for better informed and strategic decision-making.
Conclusion
Understanding the complicated world of stock trading requires a thorough understanding of both technical and fundamental studies. You must check out my book “The Investor’s Sutra” to learn more in-depth about these analyses practically and enjoyably. You will gain complete comprehension through the use of illustrations and examples.
Whether you’re a day trader who relies on technical indications or a long-term investor who examines a company’s financials, finding the appropriate balance allows you to make more educated decisions in this ever-changing financial world.


